nouveau blog
During material selection, many engineers habitually judge a polymer’s flow and processing performance based on its molecular weight. But did you know? Molecular weight alone doesn’t fully reflect a polymer’s fluidity. Especially in applications requiring precise flow control, the critical entanglement molecular weight (Mc) is the truly decisive factor.
Critical entanglement molecular weight refers to the threshold at which polymer chains begin to ‘entangle’ and form a network-like structure. Once this point is exceeded, the polymer’s fluidity drops significantly.
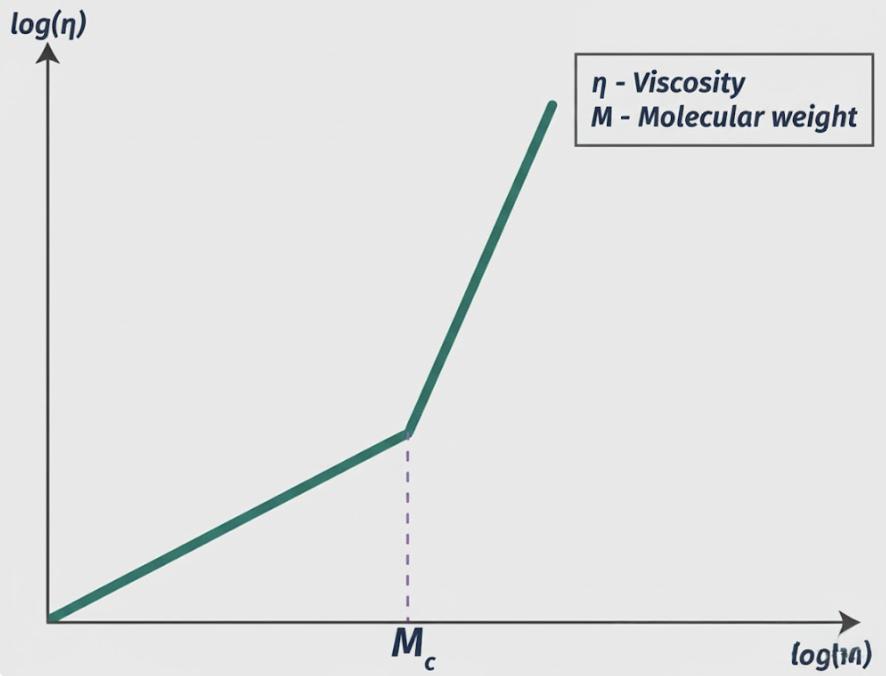
In short, Mc determines how freely polymer chains can move. Materials with poor flow usually have a low critical entanglement molecular weight , causing chains to entangle early.
Rigid polymers like PC entangle earlier, leading to a lower Mc and poorer flow.
Strong forces such as hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions (PA, PET, etc.) reduce Mc, decreasing fluidity. (Commercial PA6, however, can still flow well due to its relatively low molecular weight.)
Branched polymers reduce chain entanglement. For example, LDPE flows better due to its branched chains, while HDPE is more rigid and less fluid.
A wider distribution can reduce flow uniformity, though it may improve shear thinning in some cases.
Flexible chains flow more easily, while rigid chains hinder fluidity.
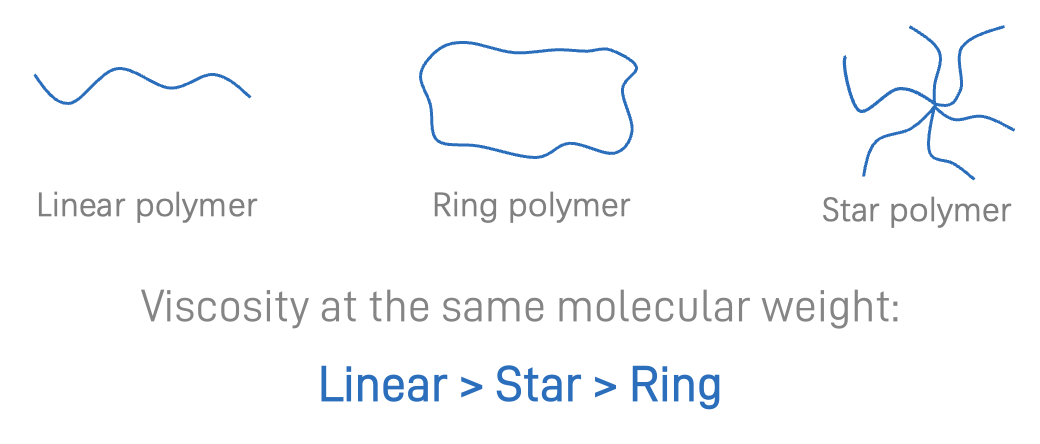
Even for polymers with the same composition and molecular weight, simpler or cyclic structures often show lower viscosity. For instance, linear polymers entangle more and have higher viscosity than cyclic ones.